Digital & Print Membership
Yearly + Receive 8 free printed back issues
$420 Annually
Monthly + Receive 3 free printed back issues
$40 Monthly
Israel’s Environmental Degradation in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria
Earth for Palestine
Introduction
Environmental degradation under occupation and apartheid often stems from military operations, resource exploitation, and infrastructural destruction. In the context of Israel’s occupation of Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria, significant environmental harm has been reported. These impacts include deforestation, pollution, depletion of water resources, and destruction of agricultural lands on top of human life loss. This report focuses and outlines the key environmental issues in these regions attributed to Israeli policies and military actions.
Environmental Impact in Palestine
Water Resource Exploitation and Pollution
Israel exerts control over most water resources in the occupied Palestinian territories. The diversion of water from the Jordan River and over-extraction from the Mountain and Coastal Aquifers has led to severe water shortages for Palestinians. Moreover, wastewater from Israeli settlements has polluted Palestinian farmlands and water sources, with untreated sewage discharged into the West Bank’s valleys and streams.
Theft of Natural Resources: Gas and Oil Exploitation
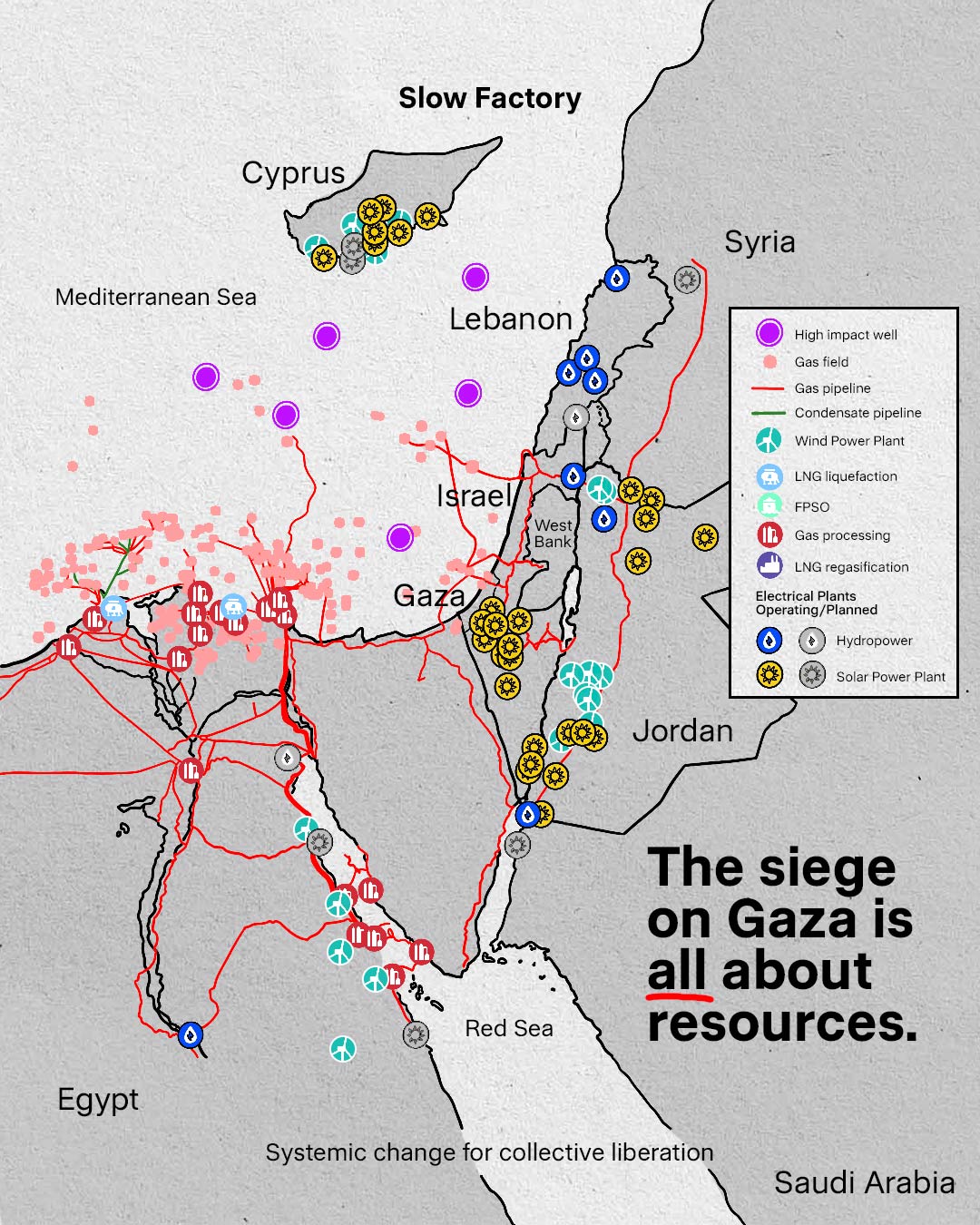
Israel has been stealing Palestinian natural resources, particularly in Gaza, where it has restricted Palestinian access to offshore gas fields. Reports indicate that Israel has taken control of gas reserves off the coast of Gaza, depriving Palestinians of their rightful resources and economic opportunities. Furthermore, Israel has shown interest in oil drilling in Gaza, raising concerns over environmental degradation and economic exploitation.
Gaza is home to significant natural gas reserves, primarily located offshore in the Mediterranean Sea. These reserves have the potential to provide Palestinians with economic independence and energy security. However, Israeli policies and military control have largely prevented Palestinians from accessing and benefiting from these resources. This section examines Israel’s exploitation of Gaza’s oil and gas reserves and the environmental, economic, and political consequences of this resource theft.
Gas Reserves in Gaza
The Gaza Marine gas field, discovered in 1999 by British Gas (BG Group), is estimated to contain over 1 trillion cubic feet of natural gas. It lies about 30 kilometers off the coast of Gaza in Palestinian territorial waters. This field could generate billions in revenue and significantly reduce Palestinian dependence on foreign energy imports. However, despite this potential, Palestinians have been denied the ability to develop and extract these resources due to Israeli restrictions.
Israeli Control and Resource Exploitation
Israel has effectively seized control over Gaza’s maritime resources, preventing Palestinian authorities from extracting gas and negotiating independent deals for its sale.
Over the years, Israel has:
-
Blocked Palestinian access to the gas field through military-enforced maritime restrictions.
-
Negotiated with international energy companies to exploit the gas without Palestinian consent.
-
Extracted gas from adjacent fields, some of which extend into Palestinian waters, depriving Gaza of its rightful share.
-
Blocked all fuel, water, food from entering Gaza for 17 months, violating International human rights law
Israeli authorities have argued security concerns as justification for these restrictions, but critics view this as part of a broader strategy to maintain economic dominance over the Palestinian territories.
Oil Exploration in Gaza
Beyond natural gas, reports indicate that Israel has explored the possibility of offshore oil drilling in Palestinian-controlled areas. While oil reserves in Gaza are less documented than its gas fields, Israeli interest in energy exploration raises concerns over further** environmental degradation and economic exploitation.**
Economic and Environmental Consequences
Economic Consequences
-
The inability to exploit its own natural gas means **Gaza remains dependent on Israeli energy supplies, **which are often restricted or cut off at whim.
-
Potential revenue from gas sales, estimated in the billions of dollars, could have funded infrastructure, healthcare, and development in Gaza.
-
Israel’s control over these resources reinforces Palestinian economic stagnation and vulnerability.
Environmental Consequences
-
Any unauthorized Israeli drilling and extraction risks polluting Gaza’s coastline and disrupting marine ecosystems.
-
Oil and gas extraction, if improperly managed, could lead to oil spills, gas leaks, and long-term ecological damage in Palestinian waters.
-
By denying Palestinians control, Israel prevents the development of environmentally sustainable energy policies in Gaza.
The case of Gaza’s oil and gas reserves highlights the broader issue of resource exploitation in occupied territories. Israel’s control over these vital energy sources has deprived Palestinians of economic independence, reinforced dependence on Israeli energy supplies, and raised concerns about environmental degradation. Addressing this issue requires international intervention and legal accountability to ensure that Palestinians regain control over their natural wealth.
Deforestation, Fruit Tree Theft, and Land Degradation
Israeli settlement expansion and military occupation have led to large-scale deforestation in Palestine. Olive groves, which are crucial for Palestinian livelihoods, have been systematically uprooted or burned by settlers and the Israeli military. Beyond destruction, reports indicate that Israeli entities have engaged in the systematic theft of Palestinian fruit-bearing trees, particularly olive trees, citrus trees, and date palms. These stolen trees are often transplanted into Israeli settlements or sold commercially for profit. The removal of these trees not only affects the Palestinian agricultural economy but also depletes the region’s biodiversity and accelerates desertification. The construction of the separation wall has further fragmented ecosystems and disrupted natural habitats, making it difficult for Palestinian farmers to access and tend to their lands.
Air and Soil Pollution
Frequent military strikes and the use of heavy artillery, including white phosphorus munitions in Gaza, have contaminated the soil and air, impacting public health and biodiversity. The destruction of waste treatment facilities in Gaza has resulted in the uncontrolled spread of hazardous materials. The use of phosphorus gas has exacerbated environmental and health risks, as it releases toxic chemicals that persist in the air and soil, further harming ecosystems and human populations.

Environmental Impact in Lebanon
Oil Spill and Marine Pollution
One of the most catastrophic environmental disasters in Lebanon occurred during the 2006 war, when Israeli airstrikes targeted the Jiyyeh power station, causing a massive oil spill along Lebanon’s Mediterranean coast. This spill devastated marine life and severely compromised the livelihoods of coastal communities dependent on fishing.
Forest Fires and Land Degradation
Israeli shelling and airstrikes have led to extensive wildfires in southern Lebanon, destroying large forested areas. These fires have further contributed to soil erosion and loss of biodiversity. The use of cluster munitions has left unexploded ordnance scattered across agricultural lands, posing risks to farmers and restricting land use.
**Phosphorus Gas Usage
**Reports indicate that Israeli forces have used white phosphorus munitions in Lebanon, particularly during the 2006 war. The use of this incendiary substance has led to severe environmental and health hazards, contaminating soil and water sources, and causing long-term ecological damage.
Effects of White Phosphorus on the Environment
Air Pollution and Toxic Emissions
When white phosphorus burns, it releases toxic phosphorus pentoxide, which reacts with moisture in the air to form corrosive phosphoric acid. This leads to:
-
Severe air pollution, particularly in areas where phosphorus munitions are used extensively.
-
Respiratory problems in exposed populations due to inhalation of toxic fumes.
-
Acidic rainfall, which can damage crops, contaminate water sources, and degrade soil quality over time.
Soil and Water Contamination
-
Phosphorus residue can seep into the soil, making agricultural land infertile and contaminating groundwater.
-
Rainwater can carry phosphorus particles into rivers and reservoirs, polluting drinking water sources.
-
Toxic runoff from phosphorus-affected areas can disrupt local ecosystems, harming wildlife and fisheries.
Human Health Consequences
It is estimated that the lethal dose of white phosphorus in humans is 0.1 grams, but even a much smaller amount can have adverse effects on people including:
-
Severe burns: White phosphorus sticks to human skin, causing deep burns that are difficult to treat.
-
Chronic respiratory diseases: Inhalation of phosphorus fumes can lead to lung damage, chronic coughing, and long-term breathing issues.
-
Neurological damage: Long-term exposure has been linked to neurological disorders and cognitive impairments.
-
Damage to vital organs: Exposure to white phosphorus is also linked to **kidney and liver failure and gastrointestinal irritation **as well.
-
Increased cancer risk: Studies suggest exposure to phosphorus combustion byproducts may increase the likelihood of certain cancers.
Measuring Air Quality in Phosphorus-Affected Areas
1. Particulate Matter (PM) Sensors – Detecting Airborne Phosphorus Particles
Example: The PurpleAir PA-II Sensor, used globally for real-time air quality monitoring, can detect fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) that may contain phosphorus residues. Similar sensors have been deployed in Gaza and Lebanon by environmental organizations to measure pollution from conflict zones.
Application in Lebanon: These sensors can be placed in bombed areas to detect phosphorus dust and track its spread. Data can help assess how far toxic particles travel and how long they remain in the air.
2. Chemical Gas Analyzers – Measuring Phosphorus Pentoxide and Acidic Compounds
Example: The Thermo Scientific Model 43i SO₂ Analyzer can measure sulfur dioxide and phosphorus oxides, which are byproducts of white phosphorus combustion. Gas analyzers like this have been used in Iraq and Syria to monitor chemical weapon residues.
Application in Lebanon: After phosphorus bombings, these analyzers can detect toxic gases lingering in the air, confirming environmental contamination and assessing health risks.
3. Satellite Imaging and Remote Sensing – Tracking Pollution and Fire-Related Emissions
Example:
-
**NASA’s MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) **has been used to monitor fire emissions and air pollution from forest fires, wars, and industrial explosions.
-
The Sentinel-5P satellite (operated by the European Space Agency) can detect airborne chemicals, including phosphorus-related pollutants.
** Application in Lebanon:**
Satellite data can show where phosphorus munitions were used, the scale of air pollution, and how long contamination persists. This method has already been used to track oil spill pollution from Israeli airstrikes on Lebanon’s Jiyyeh power plant in 2006.
**4. Groundwater and Soil Testing – Detecting Phosphorus Contamination in Land and Water
**
Example:
-
The ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) technique has been used to detect heavy metal contamination in war zones, including Gaza.
-
Lebanon’s National Council for Scientific Research (CNRS-L) has conducted soil and water quality assessments after Israeli bombings.
**Application in Lebanon: **After phosphorus munitions are used, soil and groundwater samples can be tested for phosphorus compounds. This can confirm contamination levels in farmlands and drinking water sources, affecting agriculture and human health.
International agencies, including the UN and environmental monitoring organizations, could deploy these methods to document the long-term consequences of phosphorus weapon use in Lebanon.
The use of white phosphorus by the Israeli military in Lebanon has had severe environmental, health, and ecological consequences. Toxic emissions contribute to air pollution, soil degradation, and water contamination, while exposed populations suffer from chronic illnesses and long-term health risks. Conducting air quality and soil contamination assessments is essential to quantify the full impact and push for accountability under international law.
Environmental Impact in Syria
Destruction of Agricultural Lands and Water Resource Control in Syria
Destruction of Agricultural Lands in the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights, a fertile and strategic plateau occupied by Israel since 1967, has faced extensive environmental destruction due to Israeli military operations. Syrian officials and environmental organizations have reported severe damage to farmland caused by:
- Airstrikes and Bombardment – Israeli airstrikes targeting Syrian infrastructure and military positions have also impacted farmlands, orchards, and grazing areas. Explosions cause soil degradation, destroy crops, and leave behind unexploded ordnance that makes agricultural activities hazardous.
Example: In multiple strikes on Syrian territories near the Golan Heights, Israeli missiles have set farmland ablaze, reducing agricultural productivity.
- Land Confiscation and Settlement Expansion – Israeli settlements in the occupied Golan Heights have expanded, displacing Syrian farmers and reducing the available land for local agricultural production.
Example: The Israeli government has promoted new settlements such as Trump Heights, further restricting access to farmlands for displaced Syrian families.
- Military Exercises and Land Degradation – The Israeli military frequently conducts live-fire exercises in parts of the Golan Heights, which result in:
-
Soil contamination from spent ammunition.
-
Fires caused by explosions, further damaging local ecosystems and farmland.
-
Erosion due to heavy military vehicle movement, making it harder to cultivate crops.
The destruction of Syrian farmland has led to:
Loss of food security, as Syria depends on the Golan for fruit, grains, and livestock grazing.
Economic hardship for farmers who rely on agriculture as their primary source of income.
Long-term environmental damage, including desertification and reduced soil fertility.
Water Resource Control and Its Impact on Syrian Communities
The Golan Heights is a vital water source, as it supplies the Jordan River, Yarmouk River, and Sea of Galilee, making it one of the most strategically important regions in the Middle East. Since Israel’s occupation, it has imposed severe restrictions on Syrian communities’ access to water, leading to drought and agricultural collapse. As of now, **Israel controls 40% of Jordan and Syria’s shared water resources. **
1. Israeli Control of Springs, Rivers, and Aquifers
-
The Banias and Dan Springs, which contribute to the Jordan River’s flow, have been heavily diverted by Israel.
-
The Yarmouk River, which originally supplied water to both Syria and Jordan, has been partially controlled and redirected by and to Israel, reducing both Syrian and Jordanian water availability.
2. Water Theft by Israeli Settlements
Israeli authorities are stealing water access for settlers in the Golan Heights, leaving Syrian villages with minimal or no water supply for drinking and irrigation.
Example: Syrian farmers in the Golan struggle to irrigate their fields, while Israeli settlements enjoy advanced water infrastructure for agriculture and domestic use.
3. Desertification and Agricultural Decline
-
Without sufficient water, once-fertile Syrian lands in the Golan are turning into arid wastelands.
-
Reduced water flow has led to lower crop yields and made livestock farming unsustainable.
****Deforestation and loss of vegetation due to Israeli land seizures and military actions have worsened soil erosion.
Impact on Local Farmers: Many Syrian Druze farmers in the Golan Heights have faced **increased water shortages **and have been forced to abandon their agricultural lands due to Israeli-imposed restrictions.
Political and Economic Consequences: Israel’s monopolization of Golan’s water has weakened Syrian agricultural independence and placed further strain on Syria’s war-torn economy.
Israeli policies in the occupied Golan Heights have led to the systematic destruction of agricultural lands and severe water shortages for Syrian communities. Military operations, settlement expansion, and water control measures have turned once-productive lands into **barren, drought-stricken areas.
** These actions exacerbate food insecurity, economic hardship, and environmental decline, further deepening the impact of Israel’s occupation on Syria’s rural populations.
Satellite imagery has been instrumental in documenting the environmental and infrastructural impacts of military actions in Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria. Below are specific examples illustrating these effects:
Lebanon:
-
Beirut Port Explosion (August 2020): Satellite images captured the extensive damage caused by the explosion at Beirut’s port, highlighting the widespread destruction of the surrounding area.
The Express Tribune
-
Southern Lebanon Airstrikes (2024): NASA’s Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) detected numerous heat signatures in southern Lebanon, confirming intense airstrikes that significantly impacted the region. Sensex falls over 100 pts+1www.ndtv.com+1
Palestine (Gaza Strip):
-
Destruction in Rafah (2024): Satellite imagery revealed vast destruction in Rafah following ground operations, with significant damage to residential areas and infrastructure. bellingcat
-
Widespread Damage Across Gaza (2024): Maps, charts, and satellite images demonstrated extensive damage to buildings throughout the Gaza Strip since the onset of conflict. The Express Tribune+3The Guardian+3AP News+3
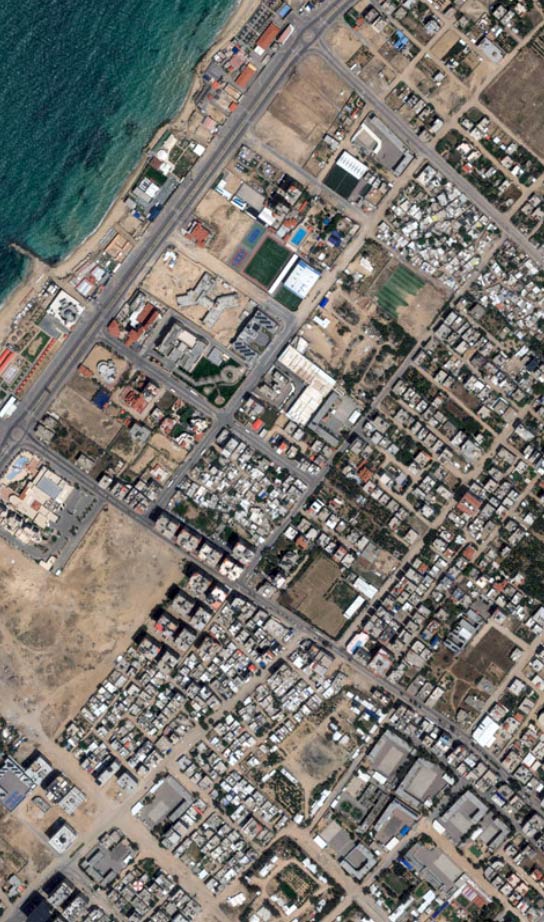
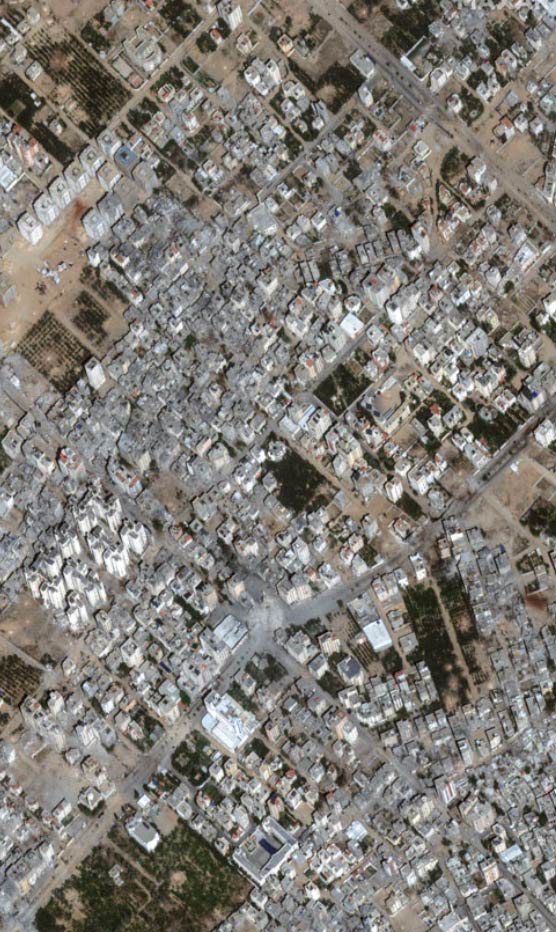


*Satellite images show destruction from Israel’s assault on Gaza *
Israel’s Actions as Ecocide: The Environmental Destruction in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria
Beyond the catastrophic loss of human life, Israel’s military actions and environmental policies amount to ecocide—the deliberate destruction of ecosystems, natural resources, and biodiversity in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria. The widespread devastation to land, water, and air in these regions has caused long-term, possibly irreversible, damage to the environment, affecting both people and wildlife for generations to come.
1. Systematic Destruction of Farmlands and Forests
Palestine (West Bank & Gaza)
-
Olive Tree Uprooting & Agricultural Sabotage: The Israeli military and settlers have destroyed over 800,000 olive trees in the West Bank since 1967. These trees are essential to Palestinian culture, economy, and environmental stability.
-
Bombing of Gaza’s Agricultural Land: Repeated aerial bombardments and shelling have burned entire farmlands, rendering them infertile due to chemical contamination from explosives.
-
Use of Herbicides to Destroy Crops: Israel has sprayed toxic herbicides along Gaza’s border, killing Palestinian crops under the pretext of clearing security zones. This has led to soil degradation, loss of biodiversity, and food insecurity.
Lebanon
-
Forest Fires Caused by Bombing: Israeli shelling in southern Lebanon has sparked wildfires that consume vast forested areas, leading to habitat loss and soil erosion.
-
**Cluster Munitions Contaminating Land: **Unexploded Israeli cluster bombs from the 2006 war still litter fields, making large areas unsafe for farming and human habitation.
Syria (Golan Heights)
-
**Deforestation and Desertification: **Israeli policies have restricted Syrian farmers’ access to their land, leading to soil degradation and loss of tree cover. The conversion of agricultural lands into Israeli military zones has resulted in mass deforestation.
-
Illegal Settler Agriculture: Israeli settlers exploit Syrian agricultural lands, redirecting water supplies for exclusive use in Israeli farms while Syrian farmers are denied access to irrigation.
2. Pollution of Water Sources and Deliberate Resource Theft
Palestine (Gaza & West Bank)
-
Water Apartheid in the West Bank: Israel diverts over 80% of Palestinian water resources for use by Israeli settlers, leaving Palestinian communities with severe water shortages.
*** Destruction of Water Infrastructure in Gaza:** Israeli airstrikes have targeted Gaza’s water desalination plants, sewage treatment facilities, and wells, causing:
- Toxic contamination of groundwater
- Severe drinking water shortages (97% of Gaza’s water is undrinkable)
- Widespread diseases due to waterborne pollution
Lebanon
-
Oil Spill Disaster from Israeli Strikes: In 2006, Israel bombed the Jiyyeh power plant, releasing 15,000 tons of oil into the Mediterranean Sea, devastating marine life and fisheries along Lebanon’s coast.
-
Targeting of Dams and Water Networks: Israeli airstrikes have damaged water infrastructure, reducing Lebanon’s access to clean water and irrigation.
Syria (Golan Heights)
-
Theft of Water Resources: Israel has diverted water from the Banias and Dan rivers, which are crucial for Syrian agriculture, while settlers receive privileged access.
-
**Water Pollution from Military Activity: **Israeli military zones in the Golan Heights have led to **chemical runoff and contamination of soil and water sources, **harming local wildlife and agriculture.
3. Air, Soil, and Chemical Contamination from Military Weapons
Phosphorus Gas and Toxic Bombardment
Israel’s use of white phosphorus munitions in Gaza and Lebanon has led to:
*Soil contamination, making agricultural land infertile
*Airborne toxic chemicals, affecting human and animal health
*Acid rain formation**, further degrading water and land quality
Long-Term Effects on Ecosystems
-
**Destruction of Pollinators (Bees, Birds, and Wildlife): **Bombings and deforestation have wiped out bee populations and migratory birds, disrupting natural pollination cycles and food production.
-
Collapse of Marine Ecosystems: The Mediterranean coast has suffered massive fish die-offs due to oil spills, phosphorus contamination, and destruction of wastewater treatment plants.
4. The Definition of Ecocide: How Israel’s Actions Qualify
Under international law, ecocide is defined as:
- “Unlawful or wanton acts committed with the knowledge that there is a substantial likelihood of severe and widespread damage to the environment.”*
Israel’s military operations and policies in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria meet this definition because:
- They systematically destroy natural ecosystems through bombings, land seizures, and resource theft.
- They disproportionately target environmental infrastructure (water plants, farmlands, forests).
- They cause long-term harm to biodiversity, food security, and climate resilience.
Holding Israel Accountable for Ecocide
The destruction of Palestinian, Lebanese, and Syrian ecosystems is not merely collateral damage but a calculated strategy of environmental warfare. By depriving communities of their lands, water, and clean air, Israel’s actions have devastating consequences for both human populations and the planet.
Call to Action:
*** International organizations and environmental watchdogs must document and prosecute ecocide crimes in conflict zones.
-
Palestinian, Lebanese, and Syrian communities deserve restoration efforts and reparations for environmental destruction.
-
Global awareness and legal frameworks must be strengthened to prevent the weaponization of nature in warfare.
**
Topics:
Filed under:
Location:
{
"article":
{
"title" : "Israel’s Environmental Degradation in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria",
"author" : "EIP Editors",
"category" : "essays",
"url" : "https://everythingispolitical.com/readings/israel-environmental-degradation-palestine-lebanon-syria",
"date" : "2025-04-10 14:16:00 -0400",
"img" : "https://everythingispolitical.com/uploads/SlowFactory_EarthPercent_Campaign-09.jpg",
"excerpt" : "Earth for Palestine",
"content" : "Earth for PalestineIntroductionEnvironmental degradation under occupation and apartheid often stems from military operations, resource exploitation, and infrastructural destruction. In the context of Israel’s occupation of Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria, significant environmental harm has been reported. These impacts include deforestation, pollution, depletion of water resources, and destruction of agricultural lands on top of human life loss. This report focuses and outlines the key environmental issues in these regions attributed to Israeli policies and military actions.Environmental Impact in PalestineWater Resource Exploitation and PollutionIsrael exerts control over most water resources in the occupied Palestinian territories. The diversion of water from the Jordan River and over-extraction from the Mountain and Coastal Aquifers has led to severe water shortages for Palestinians. Moreover, wastewater from Israeli settlements has polluted Palestinian farmlands and water sources, with untreated sewage discharged into the West Bank’s valleys and streams.Theft of Natural Resources: Gas and Oil ExploitationIsrael has been stealing Palestinian natural resources, particularly in Gaza, where it has restricted Palestinian access to offshore gas fields. Reports indicate that Israel has taken control of gas reserves off the coast of Gaza, depriving Palestinians of their rightful resources and economic opportunities. Furthermore, Israel has shown interest in oil drilling in Gaza, raising concerns over environmental degradation and economic exploitation.Gaza is home to significant natural gas reserves, primarily located offshore in the Mediterranean Sea. These reserves have the potential to provide Palestinians with economic independence and energy security. However, Israeli policies and military control have largely prevented Palestinians from accessing and benefiting from these resources. This section examines Israel’s exploitation of Gaza’s oil and gas reserves and the environmental, economic, and political consequences of this resource theft.Gas Reserves in GazaThe Gaza Marine gas field, discovered in 1999 by British Gas (BG Group), is estimated to contain over 1 trillion cubic feet of natural gas. It lies about 30 kilometers off the coast of Gaza in Palestinian territorial waters. This field could generate billions in revenue and significantly reduce Palestinian dependence on foreign energy imports. However, despite this potential, Palestinians have been denied the ability to develop and extract these resources due to Israeli restrictions.Israeli Control and Resource ExploitationIsrael has effectively seized control over Gaza’s maritime resources, preventing Palestinian authorities from extracting gas and negotiating independent deals for its sale.Over the years, Israel has: Blocked Palestinian access to the gas field through military-enforced maritime restrictions. Negotiated with international energy companies to exploit the gas without Palestinian consent. Extracted gas from adjacent fields, some of which extend into Palestinian waters, depriving Gaza of its rightful share. Blocked all fuel, water, food from entering Gaza for 17 months, violating International human rights law Israeli authorities have argued security concerns as justification for these restrictions, but critics view this as part of a broader strategy to maintain economic dominance over the Palestinian territories.Oil Exploration in GazaBeyond natural gas, reports indicate that Israel has explored the possibility of offshore oil drilling in Palestinian-controlled areas. While oil reserves in Gaza are less documented than its gas fields, Israeli interest in energy exploration raises concerns over further** environmental degradation and economic exploitation.**Economic and Environmental ConsequencesEconomic Consequences The inability to exploit its own natural gas means **Gaza remains dependent on Israeli energy supplies, **which are often restricted or cut off at whim. Potential revenue from gas sales, estimated in the billions of dollars, could have funded infrastructure, healthcare, and development in Gaza. Israel’s control over these resources reinforces Palestinian economic stagnation and vulnerability. Environmental Consequences Any unauthorized Israeli drilling and extraction risks polluting Gaza’s coastline and disrupting marine ecosystems. Oil and gas extraction, if improperly managed, could lead to oil spills, gas leaks, and long-term ecological damage in Palestinian waters. By denying Palestinians control, Israel prevents the development of environmentally sustainable energy policies in Gaza. The case of Gaza’s oil and gas reserves highlights the broader issue of resource exploitation in occupied territories. Israel’s control over these vital energy sources has deprived Palestinians of economic independence, reinforced dependence on Israeli energy supplies, and raised concerns about environmental degradation. Addressing this issue requires international intervention and legal accountability to ensure that Palestinians regain control over their natural wealth.Deforestation, Fruit Tree Theft, and Land DegradationIsraeli settlement expansion and military occupation have led to large-scale deforestation in Palestine. Olive groves, which are crucial for Palestinian livelihoods, have been systematically uprooted or burned by settlers and the Israeli military. Beyond destruction, reports indicate that Israeli entities have engaged in the systematic theft of Palestinian fruit-bearing trees, particularly olive trees, citrus trees, and date palms. These stolen trees are often transplanted into Israeli settlements or sold commercially for profit. The removal of these trees not only affects the Palestinian agricultural economy but also depletes the region’s biodiversity and accelerates desertification. The construction of the separation wall has further fragmented ecosystems and disrupted natural habitats, making it difficult for Palestinian farmers to access and tend to their lands.Air and Soil PollutionFrequent military strikes and the use of heavy artillery, including white phosphorus munitions in Gaza, have contaminated the soil and air, impacting public health and biodiversity. The destruction of waste treatment facilities in Gaza has resulted in the uncontrolled spread of hazardous materials. The use of phosphorus gas has exacerbated environmental and health risks, as it releases toxic chemicals that persist in the air and soil, further harming ecosystems and human populations.Environmental Impact in LebanonOil Spill and Marine PollutionOne of the most catastrophic environmental disasters in Lebanon occurred during the 2006 war, when Israeli airstrikes targeted the Jiyyeh power station, causing a massive oil spill along Lebanon’s Mediterranean coast. This spill devastated marine life and severely compromised the livelihoods of coastal communities dependent on fishing.Forest Fires and Land DegradationIsraeli shelling and airstrikes have led to extensive wildfires in southern Lebanon, destroying large forested areas. These fires have further contributed to soil erosion and loss of biodiversity. The use of cluster munitions has left unexploded ordnance scattered across agricultural lands, posing risks to farmers and restricting land use.**Phosphorus Gas Usage**Reports indicate that Israeli forces have used white phosphorus munitions in Lebanon, particularly during the 2006 war. The use of this incendiary substance has led to severe environmental and health hazards, contaminating soil and water sources, and causing long-term ecological damage.Effects of White Phosphorus on the EnvironmentAir Pollution and Toxic EmissionsWhen white phosphorus burns, it releases toxic phosphorus pentoxide, which reacts with moisture in the air to form corrosive phosphoric acid. This leads to: Severe air pollution, particularly in areas where phosphorus munitions are used extensively. Respiratory problems in exposed populations due to inhalation of toxic fumes. Acidic rainfall, which can damage crops, contaminate water sources, and degrade soil quality over time. Soil and Water Contamination Phosphorus residue can seep into the soil, making agricultural land infertile and contaminating groundwater. Rainwater can carry phosphorus particles into rivers and reservoirs, polluting drinking water sources. Toxic runoff from phosphorus-affected areas can disrupt local ecosystems, harming wildlife and fisheries. Human Health ConsequencesIt is estimated that the lethal dose of white phosphorus in humans is 0.1 grams, but even a much smaller amount can have adverse effects on people including: Severe burns: White phosphorus sticks to human skin, causing deep burns that are difficult to treat. Chronic respiratory diseases: Inhalation of phosphorus fumes can lead to lung damage, chronic coughing, and long-term breathing issues. Neurological damage: Long-term exposure has been linked to neurological disorders and cognitive impairments. Damage to vital organs: Exposure to white phosphorus is also linked to **kidney and liver failure and gastrointestinal irritation **as well. Increased cancer risk: Studies suggest exposure to phosphorus combustion byproducts may increase the likelihood of certain cancers. Measuring Air Quality in Phosphorus-Affected Areas1. Particulate Matter (PM) Sensors – Detecting Airborne Phosphorus ParticlesExample: The PurpleAir PA-II Sensor, used globally for real-time air quality monitoring, can detect fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) that may contain phosphorus residues. Similar sensors have been deployed in Gaza and Lebanon by environmental organizations to measure pollution from conflict zones.Application in Lebanon: These sensors can be placed in bombed areas to detect phosphorus dust and track its spread. Data can help assess how far toxic particles travel and how long they remain in the air.2. Chemical Gas Analyzers – Measuring Phosphorus Pentoxide and Acidic CompoundsExample: The Thermo Scientific Model 43i SO₂ Analyzer can measure sulfur dioxide and phosphorus oxides, which are byproducts of white phosphorus combustion. Gas analyzers like this have been used in Iraq and Syria to monitor chemical weapon residues.Application in Lebanon: After phosphorus bombings, these analyzers can detect toxic gases lingering in the air, confirming environmental contamination and assessing health risks.3. Satellite Imaging and Remote Sensing – Tracking Pollution and Fire-Related EmissionsExample: **NASA’s MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) **has been used to monitor fire emissions and air pollution from forest fires, wars, and industrial explosions. The Sentinel-5P satellite (operated by the European Space Agency) can detect airborne chemicals, including phosphorus-related pollutants. ** Application in Lebanon:**Satellite data can show where phosphorus munitions were used, the scale of air pollution, and how long contamination persists. This method has already been used to track oil spill pollution from Israeli airstrikes on Lebanon’s Jiyyeh power plant in 2006.**4. Groundwater and Soil Testing – Detecting Phosphorus Contamination in Land and Water**Example: The ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry) technique has been used to detect heavy metal contamination in war zones, including Gaza. Lebanon’s National Council for Scientific Research (CNRS-L) has conducted soil and water quality assessments after Israeli bombings. **Application in Lebanon: **After phosphorus munitions are used, soil and groundwater samples can be tested for phosphorus compounds. This can confirm contamination levels in farmlands and drinking water sources, affecting agriculture and human health.International agencies, including the UN and environmental monitoring organizations, could deploy these methods to document the long-term consequences of phosphorus weapon use in Lebanon.The use of white phosphorus by the Israeli military in Lebanon has had severe environmental, health, and ecological consequences. Toxic emissions contribute to air pollution, soil degradation, and water contamination, while exposed populations suffer from chronic illnesses and long-term health risks. Conducting air quality and soil contamination assessments is essential to quantify the full impact and push for accountability under international law.Environmental Impact in SyriaDestruction of Agricultural Lands and Water Resource Control in SyriaDestruction of Agricultural Lands in the Golan HeightsThe Golan Heights, a fertile and strategic plateau occupied by Israel since 1967, has faced extensive environmental destruction due to Israeli military operations. Syrian officials and environmental organizations have reported severe damage to farmland caused by: Airstrikes and Bombardment – Israeli airstrikes targeting Syrian infrastructure and military positions have also impacted farmlands, orchards, and grazing areas. Explosions cause soil degradation, destroy crops, and leave behind unexploded ordnance that makes agricultural activities hazardous.Example: In multiple strikes on Syrian territories near the Golan Heights, Israeli missiles have set farmland ablaze, reducing agricultural productivity. Land Confiscation and Settlement Expansion – Israeli settlements in the occupied Golan Heights have expanded, displacing Syrian farmers and reducing the available land for local agricultural production.Example: The Israeli government has promoted new settlements such as Trump Heights, further restricting access to farmlands for displaced Syrian families. Military Exercises and Land Degradation – The Israeli military frequently conducts live-fire exercises in parts of the Golan Heights, which result in: Soil contamination from spent ammunition. Fires caused by explosions, further damaging local ecosystems and farmland. Erosion due to heavy military vehicle movement, making it harder to cultivate crops. The destruction of Syrian farmland has led to:Loss of food security, as Syria depends on the Golan for fruit, grains, and livestock grazing.Economic hardship for farmers who rely on agriculture as their primary source of income.Long-term environmental damage, including desertification and reduced soil fertility.Water Resource Control and Its Impact on Syrian CommunitiesThe Golan Heights is a vital water source, as it supplies the Jordan River, Yarmouk River, and Sea of Galilee, making it one of the most strategically important regions in the Middle East. Since Israel’s occupation, it has imposed severe restrictions on Syrian communities’ access to water, leading to drought and agricultural collapse. As of now, **Israel controls 40% of Jordan and Syria’s shared water resources. **1. Israeli Control of Springs, Rivers, and Aquifers The Banias and Dan Springs, which contribute to the Jordan River’s flow, have been heavily diverted by Israel. The Yarmouk River, which originally supplied water to both Syria and Jordan, has been partially controlled and redirected by and to Israel, reducing both Syrian and Jordanian water availability. 2. Water Theft by Israeli SettlementsIsraeli authorities are stealing water access for settlers in the Golan Heights, leaving Syrian villages with minimal or no water supply for drinking and irrigation.Example: Syrian farmers in the Golan struggle to irrigate their fields, while Israeli settlements enjoy advanced water infrastructure for agriculture and domestic use.3. Desertification and Agricultural Decline Without sufficient water, once-fertile Syrian lands in the Golan are turning into arid wastelands. Reduced water flow has led to lower crop yields and made livestock farming unsustainable.****Deforestation and loss of vegetation due to Israeli land seizures and military actions have worsened soil erosion. Impact on Local Farmers: Many Syrian Druze farmers in the Golan Heights have faced **increased water shortages **and have been forced to abandon their agricultural lands due to Israeli-imposed restrictions.Political and Economic Consequences: Israel’s monopolization of Golan’s water has weakened Syrian agricultural independence and placed further strain on Syria’s war-torn economy.Israeli policies in the occupied Golan Heights have led to the systematic destruction of agricultural lands and severe water shortages for Syrian communities. Military operations, settlement expansion, and water control measures have turned once-productive lands into **barren, drought-stricken areas.** These actions exacerbate food insecurity, economic hardship, and environmental decline, further deepening the impact of Israel’s occupation on Syria’s rural populations.Satellite imagery has been instrumental in documenting the environmental and infrastructural impacts of military actions in Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria. Below are specific examples illustrating these effects:Lebanon: Beirut Port Explosion (August 2020): Satellite images captured the extensive damage caused by the explosion at Beirut’s port, highlighting the widespread destruction of the surrounding area.The Express Tribune Southern Lebanon Airstrikes (2024): NASA’s Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) detected numerous heat signatures in southern Lebanon, confirming intense airstrikes that significantly impacted the region. Sensex falls over 100 pts+1www.ndtv.com+1 Palestine (Gaza Strip): Destruction in Rafah (2024): Satellite imagery revealed vast destruction in Rafah following ground operations, with significant damage to residential areas and infrastructure. bellingcat Widespread Damage Across Gaza (2024): Maps, charts, and satellite images demonstrated extensive damage to buildings throughout the Gaza Strip since the onset of conflict. The Express Tribune+3The Guardian+3AP News+3 *Satellite images show destruction from Israel’s assault on Gaza *Israel’s Actions as Ecocide: The Environmental Destruction in Palestine, Lebanon, and SyriaBeyond the catastrophic loss of human life, Israel’s military actions and environmental policies amount to ecocide—the deliberate destruction of ecosystems, natural resources, and biodiversity in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria. The widespread devastation to land, water, and air in these regions has caused long-term, possibly irreversible, damage to the environment, affecting both people and wildlife for generations to come.1. Systematic Destruction of Farmlands and ForestsPalestine (West Bank & Gaza) Olive Tree Uprooting & Agricultural Sabotage: The Israeli military and settlers have destroyed over 800,000 olive trees in the West Bank since 1967. These trees are essential to Palestinian culture, economy, and environmental stability. Bombing of Gaza’s Agricultural Land: Repeated aerial bombardments and shelling have burned entire farmlands, rendering them infertile due to chemical contamination from explosives. Use of Herbicides to Destroy Crops: Israel has sprayed toxic herbicides along Gaza’s border, killing Palestinian crops under the pretext of clearing security zones. This has led to soil degradation, loss of biodiversity, and food insecurity. Lebanon Forest Fires Caused by Bombing: Israeli shelling in southern Lebanon has sparked wildfires that consume vast forested areas, leading to habitat loss and soil erosion. **Cluster Munitions Contaminating Land: **Unexploded Israeli cluster bombs from the 2006 war still litter fields, making large areas unsafe for farming and human habitation. Syria (Golan Heights) **Deforestation and Desertification: **Israeli policies have restricted Syrian farmers’ access to their land, leading to soil degradation and loss of tree cover. The conversion of agricultural lands into Israeli military zones has resulted in mass deforestation. Illegal Settler Agriculture: Israeli settlers exploit Syrian agricultural lands, redirecting water supplies for exclusive use in Israeli farms while Syrian farmers are denied access to irrigation. 2. Pollution of Water Sources and Deliberate Resource TheftPalestine (Gaza & West Bank) Water Apartheid in the West Bank: Israel diverts over 80% of Palestinian water resources for use by Israeli settlers, leaving Palestinian communities with severe water shortages.*** Destruction of Water Infrastructure in Gaza:** Israeli airstrikes have targeted Gaza’s water desalination plants, sewage treatment facilities, and wells, causing: Toxic contamination of groundwater Severe drinking water shortages (97% of Gaza’s water is undrinkable) Widespread diseases due to waterborne pollutionLebanon Oil Spill Disaster from Israeli Strikes: In 2006, Israel bombed the Jiyyeh power plant, releasing 15,000 tons of oil into the Mediterranean Sea, devastating marine life and fisheries along Lebanon’s coast. Targeting of Dams and Water Networks: Israeli airstrikes have damaged water infrastructure, reducing Lebanon’s access to clean water and irrigation. Syria (Golan Heights) Theft of Water Resources: Israel has diverted water from the Banias and Dan rivers, which are crucial for Syrian agriculture, while settlers receive privileged access. **Water Pollution from Military Activity: **Israeli military zones in the Golan Heights have led to **chemical runoff and contamination of soil and water sources, **harming local wildlife and agriculture. 3. Air, Soil, and Chemical Contamination from Military WeaponsPhosphorus Gas and Toxic BombardmentIsrael’s use of white phosphorus munitions in Gaza and Lebanon has led to:*Soil contamination, making agricultural land infertile*Airborne toxic chemicals, affecting human and animal health*Acid rain formation**, further degrading water and land qualityLong-Term Effects on Ecosystems **Destruction of Pollinators (Bees, Birds, and Wildlife): **Bombings and deforestation have wiped out bee populations and migratory birds, disrupting natural pollination cycles and food production. Collapse of Marine Ecosystems: The Mediterranean coast has suffered massive fish die-offs due to oil spills, phosphorus contamination, and destruction of wastewater treatment plants. 4. The Definition of Ecocide: How Israel’s Actions QualifyUnder international law, ecocide is defined as: “Unlawful or wanton acts committed with the knowledge that there is a substantial likelihood of severe and widespread damage to the environment.”*Israel’s military operations and policies in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria meet this definition because: They systematically destroy natural ecosystems through bombings, land seizures, and resource theft. They disproportionately target environmental infrastructure (water plants, farmlands, forests). They cause long-term harm to biodiversity, food security, and climate resilience.Holding Israel Accountable for EcocideThe destruction of Palestinian, Lebanese, and Syrian ecosystems is not merely collateral damage but a calculated strategy of environmental warfare. By depriving communities of their lands, water, and clean air, Israel’s actions have devastating consequences for both human populations and the planet.Call to Action:*** International organizations and environmental watchdogs must document and prosecute ecocide crimes in conflict zones. Palestinian, Lebanese, and Syrian communities deserve restoration efforts and reparations for environmental destruction. Global awareness and legal frameworks must be strengthened to prevent the weaponization of nature in warfare.** "
}
,
"relatedposts": [
{
"title" : "Seeds of Chronic Hope",
"author" : "Corinne Jabbour",
"category" : "essays",
"url" : "https://everythingispolitical.com/readings/seeds-of-chronic-hope",
"date" : "2026-03-04 12:06:00 -0500",
"img" : "https://everythingispolitical.com/uploads/Heirloom%20Corn%20at%20Buzuruna%20Juzuruna.jpg",
"excerpt" : "",
"content" : "Gathering in BeirutOn the 22nd of November 2025, a day which coincided with Lebanon’s Independence day, we gathered with a crowd at a venue facing the Beirut Port silos, which still stand half demolished, a constant reminder that our crises are in fact not tragic misfortunes, but carefully designed and manufactured atrocities. We gathered that day for the public launch of the Agroecology Coalition in Lebanon (ACL). Agroecology is not just a science or farming practices, but the movement calling for food justice and sovereignty.Mathematics of PredationThe global food system today demands that we forfeit our farmers’ rights and autonomy, our people’s dignity, health, and wellbeing, and the resilience and abundance of the environment we are a part of, all to achieve its goals. It is not driven by hatred for farmers or hatred for the environment and its people, but rather simply by the cold mathematics of this economic system that do not take things like justice, dignity, sovereignty or the health of the ecosystem into account. As a result, they are methodically sacrificed when the outcome is more profit, because this system’s one and only goal is: Ever increasing profit for ever increasing capital accumulation, no matter the cost, a fact proven yet again by today’s colonial wars, and the re-escalation of Israeli aggressions and land invasion in Lebanon.Green Colonialism in LebanonThe World Bank’s hundreds of millions of dollars in “recovery and reconstruction” loans arrive alongside efforts to redirect our production further toward export. New laws compromise seed sovereignty, threaten our cannabis heritage varieties, and surrender the autonomy of our fishermen. Layer by layer we are stripped of food sovereignty and pushed deeper into hegemonic global markets - green colonialism advancing under the banner of modernization. Our news channels are filled with the echoes of our politicians promising wealth and prosperity through global markets. These promises ignore the reality that our country’s one airport, two ports, and limited land crossings can - and have been - paralyzed by Israel within hours. They forget what happened to our imports and exports during Covid, or after the 2019 currency collapse. We grow thirsty crops that do not fill our needs but fulfill the desires of the Global North, and we send them our produce and within it our water, our labour, and the health of our land. Then to complete the dance, our government ships in food grown in poorer soil on distant land, drowning our local markets and driving our farmers into the arms of export traders, or pushing them to abandon farming and migrate to the city… As our Gibran once wrote, “Woe to a nation that eats what it does not grow!”The Trap of Conventional AgricultureOur farmers are coerced into buying hybrid seeds, synthetic chemical fertilizers, biocides (pesticides, fungicides, herbicides, rodenticides…), and other inputs at prices controlled by multinational corporations and their local allies. They sell their crops at prices controlled by traders in the wholesale markets, prices so low they barely cover their costs!“Being a farmer is like being in love with a bad woman, the whole world will tell you she is bad but all you see is the beauty in her!” This was the reply of Georges, a seasoned farmer from a mountain village in the Chouf, when I asked him why he still chooses to be a farmer one disappointing season after another. As we walked through his terraces he told me some stories: “We used to sprinkle grains on the snow, to help the birds through the harsher days of winter… My father would tell us to skip harvesting some of the fruits on the high branches of the trees, he would say that those were the share of the birds from this season!” How did capitalism succeed at slowly eroding our worldview, where we shared our harvest with the birds? How far can this love for the land and its abundance carry our increasingly burdened growers? How long can they stand in the face of the scourge of the industrial model of food production that has invaded our way of life?Our farmers are stuck in a rat race, bullied into finding ways to intensify production with every season. Instead of fair distribution where farmers get their fair share, the only choice this system offers them is: “We will take the largest share of the profit generated by your hard labour, but if you keep finding ways to produce more, the small percentage we allow you to keep might become enough for you.” The outcome is farmers under tremendous pressure to produce more, better, and faster, and that intensification requires more and more synthetic chemicals!As for people who are choosing what to eat, they find themselves with limited choices, mostly laced with toxins, because within this system, clean and nutritious food has become a luxury! Beyond human health, these intensive production methods and long-distance transportation are crumbling our entire ecosystem and massively contributing to climate change, the consequences of which we are all experiencing, from unpredictable and extreme weather, to raging wildfires and prolonged droughts. Our farmers are among those paying the highest price for this change!A System of OppressionThis system, in complicity with our local varieties of comprador aspiring billionaires, continues to turn every right that we have, every care we offer each other, every abundance we receive from nature, into commodities to be bought and sold for profit. Today’s realities in the Global South are living testament to the price that the many have to pay in service of the few, and we are the many!We reject attempts to depoliticize food, we reject attempts to sanitize this predatory dynamic with performative gestures and token measures. The charades of charity and benevolence have long expired. These tools of neo-colonialism are now seen for what they are, instruments of oppression and hegemony. We do not need an invitation to drown further in debt through loans offered under the guise of development and recovery by the same powers that fund, arm and enable the Zionist colonial project that brings on that destruction. This system has exposed itself through its oppression and subjugation of nature, women, and colonized peoples. Through military complexes, genocides, sanctions, poverty, and famine, it leaves devastation in the wake of its hollow promises of prosperity through progress and development.Tangible AlternativesWhat brought us together that day in Beirut was not just a common perspective on the root of the so-called “crises”, but a shared conviction that this system is dying, and that real, tangible, solid alternatives already exist. Alternatives that spring from the ground and require change on all levels, including the political level. Alternatives that converge the world into ways of life that prioritize human wellbeing, dignity, and harmony with the planet that is our home.For the food system, one such alternative is Agroecology, the fundamental pillar of food sovereignty. It is not just a set of farming practices or the science behind them, agroecology is a social movement that places the autonomy of small scale farmers at its center, embraces traditional knowledge, and adopts democratic and horizontal methods for governance and knowledge transfer. It is a roadmap, not for superficial reform, but for radical transformation from exploitation to sovereignty. We need to liberate our commons, our seeds, our water, our land, our spaces, our festivals, our ancestral knowledge and worldview. We need to meet our growers, trust and support them. We need to rebuild resilience into our food system in preparation for the inevitable changes that have already begun to impact our food production. We need to decentralize our seed banks, our power sources, and our decision making. Systems such as seed harvesting and propagation have been managed collectively by farmers ever since agriculture was born in our fertile crescent, it is our treasured pool of biodiversity that should not be handed over to corporations. Intellectual property rights over seeds are the equivalent of visiting the ruins of Baalbek, installing a gate at the entrance, and claiming that the ruins are now yours because of that final modification! The absurdity of this system is not lost on us.The time has come to reclaim food, health, ecosystem, and lives with dignity, for ALL people, not SOME people, as rights and not as commodities for sale! The time has come to decolonize our food, to delink ourselves from this parasitic system that has been bleeding us dry for decades, and will not stop until it starves the world, and the last bird on the last tree goes silent.We gathered that day, not for romantic ideals, but a concrete political project, a vision, and a battle for liberation that we do not wage alone. We are part of a global and widespread movement that includes farmers, peasants, and peoples everywhere, all clearly and loudly united in their categorical demand for their fundamental right to food sovereignty!Chronic HopeAfter the day had ended, with smiles, inspiration, and a warm atmosphere of camaraderie, while walking away from that venue and passing by the remains of the silos, the walk took me back 5 years, where I took those same steps after the Beirut Port explosion. I had been walking and looking around at the destruction with tears blurring my vision and silently rolling down my cheeks. I remember looking down at the ground and finding seeds in the corner where the sidewalk meets the shoulder of the road. The pods on the trees had popped open at the pressure of the explosion, spreading their seeds everywhere along with the shattered glass and rubble. I couldn’t help smiling through my tears, smiling and thinking: “We are those seeds, and we will never stop bringing life back into the death that is brought upon us.”"
}
,
{
"title" : "When Sufien Met Nefisa: An Excerpt from 'Paradiso 17' by Hannah Lillith Assadi",
"author" : "Hannah Lillith Assadi",
"category" : "excerpts",
"url" : "https://everythingispolitical.com/readings/when-sufien-met-nefisa",
"date" : "2026-03-03 11:26:00 -0500",
"img" : "https://everythingispolitical.com/uploads/Assadi.jacket.jpg",
"excerpt" : "This is an excerpt from Paradiso 17, a new novel by Hannah Lillith Assadi, which maps the journey of a Palestinian boy, Sufien, through exile from his homeland to the Middle East, Europe, and then America. This particular moment is from his time in Kuwait and his first experience with young love. Excerpted by permission of Alfred A. Knopf, a division of Penguin Random House LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this excerpt may be reproduced or reprinted without permission in writing from the publisher.",
"content" : "This is an excerpt from Paradiso 17, a new novel by Hannah Lillith Assadi, which maps the journey of a Palestinian boy, Sufien, through exile from his homeland to the Middle East, Europe, and then America. This particular moment is from his time in Kuwait and his first experience with young love. Excerpted by permission of Alfred A. Knopf, a division of Penguin Random House LLC. All rights reserved. No part of this excerpt may be reproduced or reprinted without permission in writing from the publisher.What Sufien always remembered about Kuwait was the voice of the Gulf, that rolling tongue, languorous and all-knowing, like the voice of the divine.The new house, his father’s, recently built by the government, stood alone. Sufien was accustomed to stone walls, stone ceilings, the musty smell of old buildings. This place was echoey, almost alien in its bigness. The most unfamiliar part was its modern electricity. Sufien had been raised by candlelight. Walking outside and looking up, he saw the constellations spread out like cities in every direction. Sufien had never seen a night like this. It was so dry, and he was so thirsty. This was the loneliest part of the desert: the clarity of the sky. There was no blanket. No hills, no trees. The land was just exposed to the beyond. Sometimes Sufien could hear the din of some distant party carried across the dunes, which made him think, maybe that better place is just there. What he learned in time, though, was that the desert carried sounds for miles. By the time that happier gathering reached his ear, it was just a ghost. What he missed again, what he missed forever, was the camp—that camp at the end of the world back in Syria. And now all there was in the night after all of his little brothers and sisters were asleep—there were seven of them now—and after even his parents had fallen asleep, was Sufien, alone, trying to shut his eyes despite the moan of the wind in the sand. He had stayed up with the night from a very young age, and always would. Night was the texture of his soul.There were other problems for Sufien in Kuwait. The schoolmaster belittled his Palestinian dialect, and made him sit apart from the other students. This sense of deprivation only made Sufien more willful. So he conquered algebra. Sufien understood even then that math was the only language which had completely evaded human evil even if it might be used to forward it. Once it was clear he had excelled beyond any other pupil, studying calculus by the equivalent of the eighth grade, he looked for other pathways to excellence. None of the other Kuwaiti pupils could speak English fluently, for instance, nor had anyone else memorized as many verses of the Quran. None except Nefisa.Nefisa was from Haifa, a girl of the sea, not the Gulf but Sufien’s sea, the Mediterranean, the sea which had informed the blood of his ancestors. She had his people’s eyes, the eyes of a lion, hazel, that whirl of blue, and silky dark hair, and when she was deep in thought over an equation or reciting a script of ancient poetry, she cupped her hands across her brow and squinted like she was trying to see something far into the distance. It was the first time Sufien recognized beauty. He was only thirteen, but he felt the pain of it, the inability to hold on to it, the way it could simultaneously exist and not be grasped. A thing, a real thing, was something a person could touch, point to, like a soccer ball, or his mother’s hand, or a dinar. Whereas Nefisa smelled of rain, which he had scarcely felt or seen in the years since they came to Kuwait. When she passed Sufien in the hall or on the way to the car which always waited for her after school, a 1953 baby blue Volvo station wagon, her father’s, the same model Sufien’s own father had but in turquoise, he smelled off of her a yearning petrichor, that perfume of the desert.There had to be some way to keep her, or rather keep what he felt when he beheld her. Keep it still. Keep it forever. Keep beauty. Thinking of Nefisa, the curl of her words when she recited the Quran in his own accent, or seeing the way her breasts had risen under her shirt, the fabric of her hair, like velvet, he felt like something was slipping from his grasp. Like he needed more time, more pages, more words. The poet’s curse had stricken him.The present, that enviable superpower of childhood, had abandoned him, and now he understood time and space. If she left him, if Nefisa escaped his gaze, as she did every day, if she removed herself beyond the steel doors of that station wagon, and disappeared from view, then everything would. He understood missing. Yes, this was first love. There is no difference between it and an encounter with death but a degree of charm.Sufien, Nefisa said one day. Oh, can you hear it, the voice of a pubescent girl? Shaky and sweet. She said, Walk me home. But what did Sufien know of love and how much it could hurt? To be face-to-face with desire? Almost no one of us can handle it even once we’ve known it and known it again. He looked at her and knew she could see him. Too much of him. He felt naked. So he ran ahead of her toward his father’s house.From that day onward, Sufien avoided Nefisa. It was simpler not to behold her, the gentleness of her cheekbones, the sad curvature of her mouth. She was like a tiny adult already, mourning the heaviness of the life she would later live. Her parents would be killed in the war to come once they returned to Palestine. And she would be a refugee once more, in Gaza. She would never marry, and never bear children. And on her final evening, she would walk into the sea. So they would find her like that, thrown out, half buried in the sand, after some great final exhale.Meanwhile Sufien regretted what he had not said to Nefisa for so long that it burrowed deeply inside of him. He had loved her; he had loved her purely. But he was just thirteen then. He had not yet had the courage to feel something so big.They say Allah works in mysterious ways, but everyone forgets to say how beautiful are His mysteries.Sufien might have expected his mother or his father to be the ones to greet him on his way to the land of the dead all those decades later. It would be Nefisa. When they were finally rejoined, he was no longer thirteen, but a shriveled old man, a hundred pounds of failed flesh clinging to his skeleton, his body undone by cancer, drool falling down his face. Whereas there she was, more beautiful than he had ever seen her, a grown woman, and also the child he had known, the way people can be all things at once in a dream. She was like the archetypal fool, sitting there at the pool, or was it the spring on Jebel Kan’aan, or was it the Sea of Galilee?, dipping her toes into the everlast- ing water, splashing about, a being even younger than a toddler, and likewise timelessly old.Nefisa, Nefisa, Nefisa, he would whisper. Is it you?She would say, Come, walk me home."
}
,
{
"title" : "Nature As the Battlefield: Ecocide in Lebanon and Corporate Empire",
"author" : "Sarah Sinno",
"category" : "essays",
"url" : "https://everythingispolitical.com/readings/ecocide-lebanon-chemical-warfare",
"date" : "2026-02-25 15:16:00 -0500",
"img" : "https://everythingispolitical.com/uploads/PHOTO-2026-02-25-13-34-24%202.jpg",
"excerpt" : "",
"content" : "Photo Credit: Sarah SinnoOn February 2, the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL)issued a statement announcing that Israeli occupation forces had instructed their personnel to remain under cover near the border between south Lebanon and occupied Palestine. They were ordered to keep their distance because the IOF had planned aerial activity involving the release of a “non-toxic substance.” Samples collected and analyzed by Lebanon’s Ministries of Agriculture and Environment, in coordination with the Lebanese Army and UNIFIL, confirmed that the substance sprayed by Israel was the herbicide, glyphosate. Laboratory results showed that, in some locations, concentration levels were 20 to 30 times higher than normal. Not to mention, this is not the first instance of herbicide spraying over southern Lebanon, nor is the practice confined to Lebanon. Similar tactics have been documented in Gaza, the West Bank, and Quneitra in Syria.While the IOF didn’t provide further explanation as to its purpose, these operations are part of a broader Israeli strategy to establish so-called “buffer zones” by dismantling the ecological foundations upon which communities depend. The deployment of chemical agents kills vegetation, producing de facto “security” no-go areas that empty entire regions of their Indigenous inhabitants. Cultivated fields are deliberately destroyed, soil fertility declines, and water systems become polluted. Farmers lose their livelihoods, and communities are forcibly uprooted. Demographic realities are reshaped, and space is incrementally cleared for future settlers. Simply put, these tactics function as a mechanism of displacement, dispossession, and elimination—and are importantly part of a long history of this kind of colonial territorial engineering.Glyphosate and Ecological HarmFor decades, glyphosate has been marketed as a formulation designed to kill weeds only and increase crop yields. But the consequences of its use on humans and the environment cannot be ignored: In 2015, Glyphosate was classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as “probably carcinogenic to humans,” and it has been associated with a range of additional health risks, including endocrine disruption, potential harm to reproductive health, as well as liver and kidney damage. In November of last year, the scientific journal Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology formally withdrew a study published in 2000 that had asserted the chemical’s safety.Beyond its human health implications, glyphosate is ecologically harmful. Studies have shown that it degrades soil microorganisms; others have linked it to increased plant vulnerability to disease. It can also leach into water systems, contaminating surface and groundwater sources. Exposure may be lethal to certain species like bees. Even when it does not cause immediate mortality, glyphosate eliminates vegetation that provides habitat and shelter for bees, birds, and other animals, disrupting food webs and ecological balance. What’s more, research indicates that glyphosate can alter animal behavior, affecting foraging and feeding patterns, anti-predator responses, reproduction, learning and memory, and social interactions.Despite a growing body of scientific literature highlighting its risks to both human health and the environment, and bearing in mind that corporate giants manufacturing such products have been known to fund and even ghostwrite research to promote the opposite, glyphosate remains the most widely used herbicide globally.The Monsanto ModelTo understand how it became so deeply entrenched, normalized within agriculture systems in some contexts, and used as a weapon of war in others, it is necessary to look more closely at the corporation responsible for its global expansion: Monsanto.Founded in 1901, Monsanto’s corporate history reflects a longstanding pattern of chemical production linked to environmental devastation. Over the past century, the corporation has manufactured products later proven harmful and has faced tens of thousands of lawsuits, resulting in billions of dollars in settlements.Among the products it manufactured were polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), synthetic industrial chemicals that were eventually banned worldwide due to their toxicity. Through their production and disposal, including the discharge of millions of pounds of PCBs into waterways and landfills, Monsanto contributed to some of the most enduring chemical contamination crises in modern history, the consequences of which continue to reverberate today.One of the most notorious cases unfolded in Anniston, Ala., where Monsanto’s chemical factory polluted the entire town from 1935 through the 1970s, causing widespread harm to the community. Despite being fully aware of the toxic effects of PCBs, the company concealed evidence, according to internal documents, a conduct that reflects a longstanding pattern of disregard for both environmental care and human health. Whether in the case of PCBs or glyphosate, the underlying logic remains consistent: ecological systems and communities are harmed in order to prioritize profit and, at times, territorial expansion.Monsanto also became the world’s largest seed company. Through the enforcement of restrictive patents on genetically modified seeds, the corporation consolidated unprecedented control over global food systems. By prohibiting seed saving, a practice upheld by farmers and Indigenous communities for millennia, it undermined seed sovereignty and compelled farmers to purchase new seeds each season rather than replanting from their own harvests. What had long functioned as part of the commons since the origins of human civilization, the foundational basis of food and life itself, was privatized. Monsanto transferred control over seeds from cultivators to corporations, further creating systems of structural dependency.What was once embedded in reciprocal relationships between land, seed, and cultivator is now controlled by the same chemical-producing corporations implicated in the degradation of land—as is the case of what is unfolding in southern Lebanon. Power is thus consolidated within an industrial architecture that, at times, prohibits the exchange and regeneration of seeds and, at other times, renders the land uninhabitable. In both cases, it undermines the ability to grow food and remain rooted in the land, thereby threatening the conditions necessary for survival.Chemical WarfareAlongside its record of manufacturing carcinogenic products, dumping hazardous chemicals into the environment, and contributing to the destruction of agricultural systems, Monsanto has also been linked to chemical warfare. During the Vietnam War (1962–1971), it was among the U.S. military contractors that manufactured Agent Orange, a defoliant used to strip forests and destroy crops that provided cover and food to Vietnamese communities.The chemical contained dioxin, one of the most toxic compounds known, contributing to the defoliation of millions of acres of forest and farmland. It has been associated with hundreds of thousands of deaths and long-term illnesses, including cancers and birth defects.Although acts of ecocide long predated this period, well before the term itself was coined, it was in the aftermath of Agent Orange that the word “ecocide” was first used to describe the deliberate destruction of ecosystems and began to enter political and legal discourse.The Vietnam War exposed a structural link between chemical production, corporate power, and a military doctrine in which ecosystems and farmlands are targeted precisely because they sustain human life. Nature, because it nourished, protected, and anchored Indigenous communities, was treated as an obstacle to military and imperial control. As a result, it became a battlefield in its own right.Capital and RuinThis historical precedent continues to reverberate today in Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria. Decades apart, these are not isolated acts of ecological destruction but part of a continuous trajectory carried out by the same imperial, corporate, and financial machinery.In 2018, Monsanto was acquired by Bayer. Bayer’s largest institutional shareholders include BlackRock and Vanguard, the world’s two largest asset management firms.Both firms have been identified in reports, including those by UN Special Rapporteur Francesca Albanese, as major investors in corporations linked to Israel’s occupation apparatus, military industry, and surveillance infrastructure. These include Palantir Technologies, Lockheed Martin, Caterpillar Inc., Microsoft, Amazon, and Elbit Systems.Mapping these financial linkages reveals how ecocide is structurally embedded within broader systems of violence that are deeply entrenched and mutually reinforcing. Ecocide and genocide are financed through overlapping capital networks that connect chemical production, militarization, and territorial control.The spraying of glyphosate over agricultural land in southern Lebanon must therefore be situated within this historical continuum. The same corporate-financial structure that profits from destructive chemicals and agricultural control is interwoven with the industries that maintain a settler-colonial stronghold."
}
]
}






